Pain is a universal human experience that can be caused by a wide range of factors such as injury, illness, or chronic conditions. For thousands of years, humans have been seeking ways to relieve pain and improve their quality of life. One of the most common methods used for pain management is analgesia. In this blog post, we will explore what analgesia is, its different types, and how it works to provide relief from pain.
Definition of Analgesia
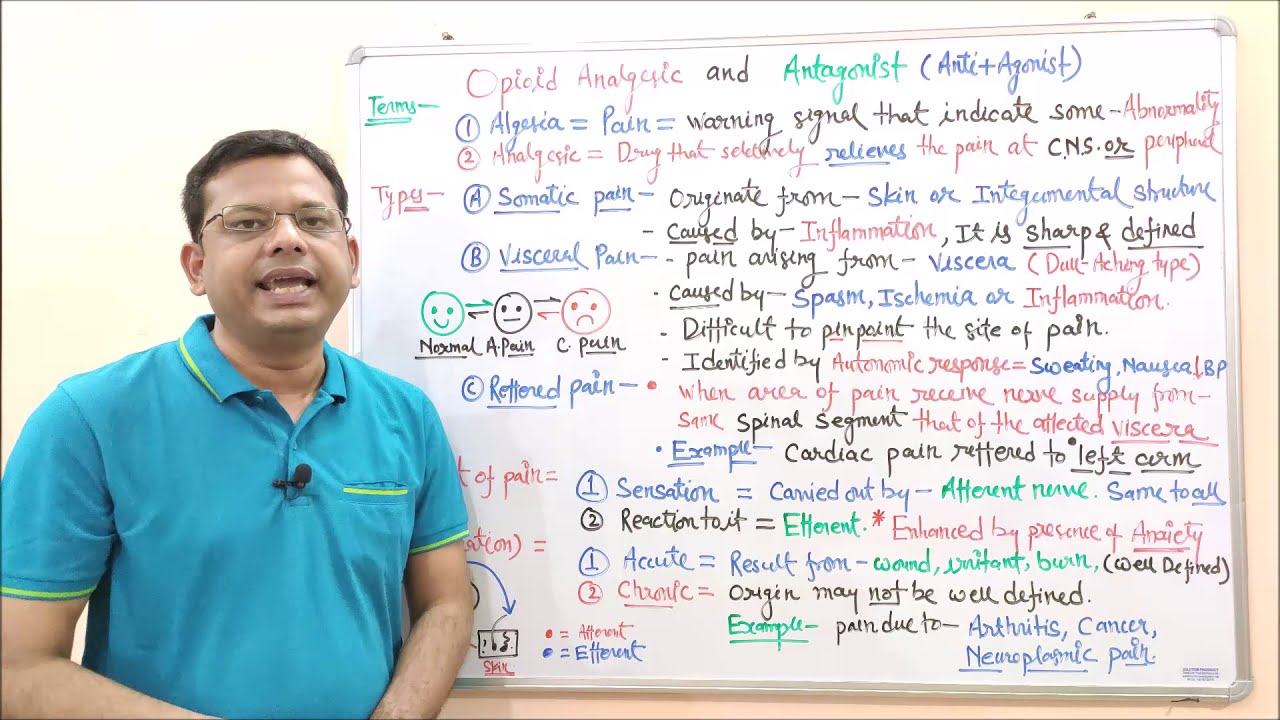
Analgesia, also known as pain relief, is the reduction or elimination of pain sensations in the body without loss of consciousness. The word “analgesia” is derived from two Greek words – “an” meaning without and “algesia” meaning sensitivity to pain. This method of pain management is commonly used in hospitals, clinics, and even at home to help individuals cope with acute or chronic pain.
There are various forms of analgesia, including medications, non-pharmacological techniques, and nerve blocks. Each type has its own specific mechanism of action and benefits. Let’s dive into the different types of analgesia and their uses.
Types of Analgesia

Pharmacological Analgesia
This type of analgesia involves the use of medication to reduce or eliminate pain. Pharmacological analgesia can be classified into two main categories: non-opioid and opioid analgesics.
Non-Opioid Analgesics
Non-opioid analgesics, also known as non-narcotic analgesics, are medications that work by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for pain and inflammation in the body. These medications include over-the-counter drugs such as aspirin, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen. They are often used to treat mild to moderate pain caused by conditions such as headaches, muscle aches, and menstrual cramps.
While non-opioid analgesics are effective for certain types of pain, they can also have side effects such as stomach upset, liver damage, or bleeding. It’s important to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional before taking these medications.
Opioid Analgesics
Opioid analgesics, also known as narcotic analgesics, are medications derived from opium that work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking pain signals. These medications include morphine, codeine, and oxycodone, and are commonly used for severe pain management.
Due to their potency, opioid analgesics have a high risk of addiction and abuse. They can also cause side effects such as constipation, drowsiness, and slowed breathing. As a result, they are often prescribed for short periods of time and under close supervision.
Non-Pharmacological Analgesia
Non-pharmacological techniques involve using methods other than medication to relieve pain. These techniques can be used alone or in combination with pharmacological methods to enhance pain relief. Some common forms of non-pharmacological analgesia include:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy involves using exercises, stretches, and other physical techniques to manage pain and improve mobility. For example, individuals with chronic back pain may benefit from a customized exercise program designed by a physical therapist to strengthen their core muscles and improve posture, reducing pain in the long term.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to stimulate the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, and improve blood circulation. While there is limited scientific evidence to support its effectiveness, many people report positive results from acupuncture for pain relief.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
TENS is a technique that uses a small, battery-operated device to deliver electrical impulses to the nerves in the affected area. This stimulation is thought to block pain signals and increase endorphin production, providing relief from pain. TENS devices can be used at home and are often recommended for chronic pain conditions such as arthritis and neuropathy.
Nerve Blocks
Nerve blocks involve injecting medication directly into or near a nerve to temporarily block pain signals. This method can provide targeted and immediate pain relief, making it useful for procedures such as labor and delivery or surgery. Nerve blocks can also be used for chronic pain management, such as in individuals with sciatica or shingles.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action for analgesia varies depending on the type used. However, the goal of all forms of analgesia is to reduce or eliminate pain sensations in the body. Some common ways in which different types of analgesia work are:
- Non-opioid analgesics: These medications work by inhibiting an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for producing prostaglandins. By blocking this enzyme, non-opioid analgesics can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Opioid analgesics: These medications work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking the transmission of pain signals. They can also increase the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter known to produce feelings of pleasure and reward.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to relieve pain by improving muscle strength, flexibility, and range of motion, reducing the strain on painful areas of the body.
- Acupuncture: The insertion of needles at specific points on the body is believed to stimulate the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms, including the release of endorphins.
- TENS: Electrical impulses delivered by TENS devices can interfere with pain signals and stimulate the release of endorphins, providing pain relief.
- Nerve blocks: By injecting medication near a nerve, nerve blocks can temporarily block pain signals, providing immediate pain relief.
Common Uses and Indications
Analgesia is used for a variety of conditions and situations, including:
- Post-surgical pain management
- Acute injuries such as broken bones or burns
- Chronic pain conditions such as arthritis and fibromyalgia
- Migraines and headaches
- Labor and delivery
- Cancer pain
In addition to its use in medical settings, analgesia can also be used at home for minor aches and pains or to manage chronic pain conditions. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any form of analgesia, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Benefits of Analgesia
The main benefit of analgesia is its ability to provide relief from pain. By reducing pain sensations, individuals can experience improved quality of life and better physical functioning. Other potential benefits of analgesia include:
- Reduced risk of complications: Uncontrolled pain can lead to a range of complications, such as decreased mobility, increased risk of infection, and poor healing. By effectively managing pain, analgesia can help to prevent these complications.
- Improved mental well-being: Chronic pain can take a toll on an individual’s mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. By reducing pain, analgesia can improve an individual’s overall mental well-being.
- Increased participation in daily activities: Pain can limit an individual’s ability to carry out daily tasks and participate in activities they enjoy. By providing pain relief, analgesia can allow individuals to engage in activities and live a more fulfilling life.
- Fewer side effects compared to other pain management methods: Compared to other pain management methods such as surgery or long-term use of opioids, analgesia has fewer potential side effects and risks.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While analgesia is generally safe and effective when used properly, it can also have potential side effects and risks. These may vary depending on the type of analgesia used, the dosage, and an individual’s health condition. Some common side effects of analgesia include:
- Stomach upset
- Drowsiness
- Headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Allergic reactions
- Addiction (with opioid analgesics)
It’s important to discuss any potential side effects with a healthcare professional before using analgesia. In addition, individuals should follow recommended dosage guidelines and never exceed the prescribed amount.
Comparisons with Other Pain Management Methods
There are various methods of pain management available, and each has its own benefits and drawbacks. Some common methods used for pain management include:
- Surgery: Surgical procedures can be effective in treating certain types of pain caused by structural problems such as herniated discs or injured joints. However, surgery carries risks and is not always necessary for pain relief.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve physical functioning and provide pain relief without the use of medications. However, it may not be as effective for severe or chronic pain.
- Chiropractic care: Chiropractors use spinal manipulation techniques to relieve pain and improve the body’s natural healing abilities. However, its effectiveness for pain relief is still being studied.
- Exercise and movement: Low-impact exercises such as yoga and swimming can help to improve pain symptoms and increase mobility. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with severe pain or limited mobility.
- Mind-body techniques: Techniques such as meditation, relaxation, and mindfulness have been shown to reduce pain symptoms and improve mental well-being. However, they may not provide immediate pain relief and require regular practice.
- Surgery: While surgery can be effective in treating certain types of pain, it carries risks and may not be necessary for all cases.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate method of pain management for your individual needs.
Guidelines for Safe Use
To ensure safe and effective use of analgesia, here are some important guidelines to keep in mind:
- Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any form of analgesia.
- Follow recommended dosage instructions and never exceed the prescribed amount.
- Be aware of potential interactions with other medications or health conditions.
- If using opioids, do not take more than prescribed and do not share your medication with others.
- Keep track of your pain symptoms and report any changes or concerns to your healthcare professional.
- Store medications safely and out of reach of children.
- If experiencing any side effects, contact your healthcare professional immediately.
Recent Advances and Research in Analgesia
In recent years, there have been numerous advancements and research studies on analgesia. Some promising areas of development and research include:
- Development of non-opioid analgesics: With the growing concern around opioid addiction and abuse, there has been an increased focus on developing non-opioid analgesics that can provide similar levels of pain relief without the risk of addiction.
- Targeted drug delivery systems: Researchers are working on ways to deliver medication directly to the affected area, reducing the risk of side effects and increasing the effectiveness of analgesia.
- Alternative methods of pain management: As mentioned earlier, there is ongoing research into non-pharmacological alternatives for pain management, including virtual reality therapy, music therapy, and hypnotherapy.
- Personalized medicine: With advancements in genetics and technology, researchers are exploring ways to use an individual’s genetic makeup to determine the most effective type and dosage of analgesia for pain relief.
Practical Tips for Effective Pain Management
In addition to using analgesia, there are other steps individuals can take to effectively manage their pain and improve their quality of life. Some practical tips for pain management include:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress can all help to reduce pain symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Practice good sleep hygiene: Adequate sleep is essential for pain management. Try to establish a regular sleep routine and create a comfortable sleep environment.
- Use heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can provide temporary pain relief.
- Seek support: Chronic pain can be physically and emotionally taxing. It’s important to seek support from friends, family, or a therapist to help cope with the challenges of living with pain.
Conclusion
Pain is an inevitable part of life, but it doesn’t have to control our lives. With the use of analgesia, individuals can experience relief from pain and improve their physical and mental well-being. Understanding the different types of analgesia, their mechanisms of action, and potential risks and benefits is crucial for safe and effective use. By following recommended guidelines and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can find relief from pain and improve their quality of life.
