As the world continues to embrace the digital age, the importance of digital literacy has become increasingly evident, particularly in the realm of online learning. Digital literacy encompasses the skills and knowledge required to effectively navigate, utilize, and create digital content in a variety of contexts. In the context of online learning, the assessment of digital literacy is crucial for ensuring that students are equipped with the necessary skills to succeed in their academic endeavors.
Definition and Importance of Digital Literacy in Online Learning
Understanding Digital Literacy
Digital literacy is the ability to use, understand, and create digital content effectively and responsibly. It encompasses a wide range of skills, including information and communication technology (ICT) proficiency, critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration in digital environments.
The Significance of Digital Literacy in Online Learning
In the digital age, online learning has become a prevalent mode of education, offering flexibility, accessibility, and a wealth of resources. However, the success of online learning is heavily dependent on the digital literacy of the students. Effective digital literacy skills enable students to:
- Navigate and utilize online platforms and learning management systems
- Access, evaluate, and synthesize digital information
- Engage in online discussions and collaborations
- Create and present digital content
- Demonstrate proficiency in using various digital tools and applications
By assessing and addressing digital literacy, educators can ensure that students are equipped with the necessary skills to thrive in the digital learning environment, leading to improved academic outcomes and overall success.
Key Components of Digital Literacy Skills
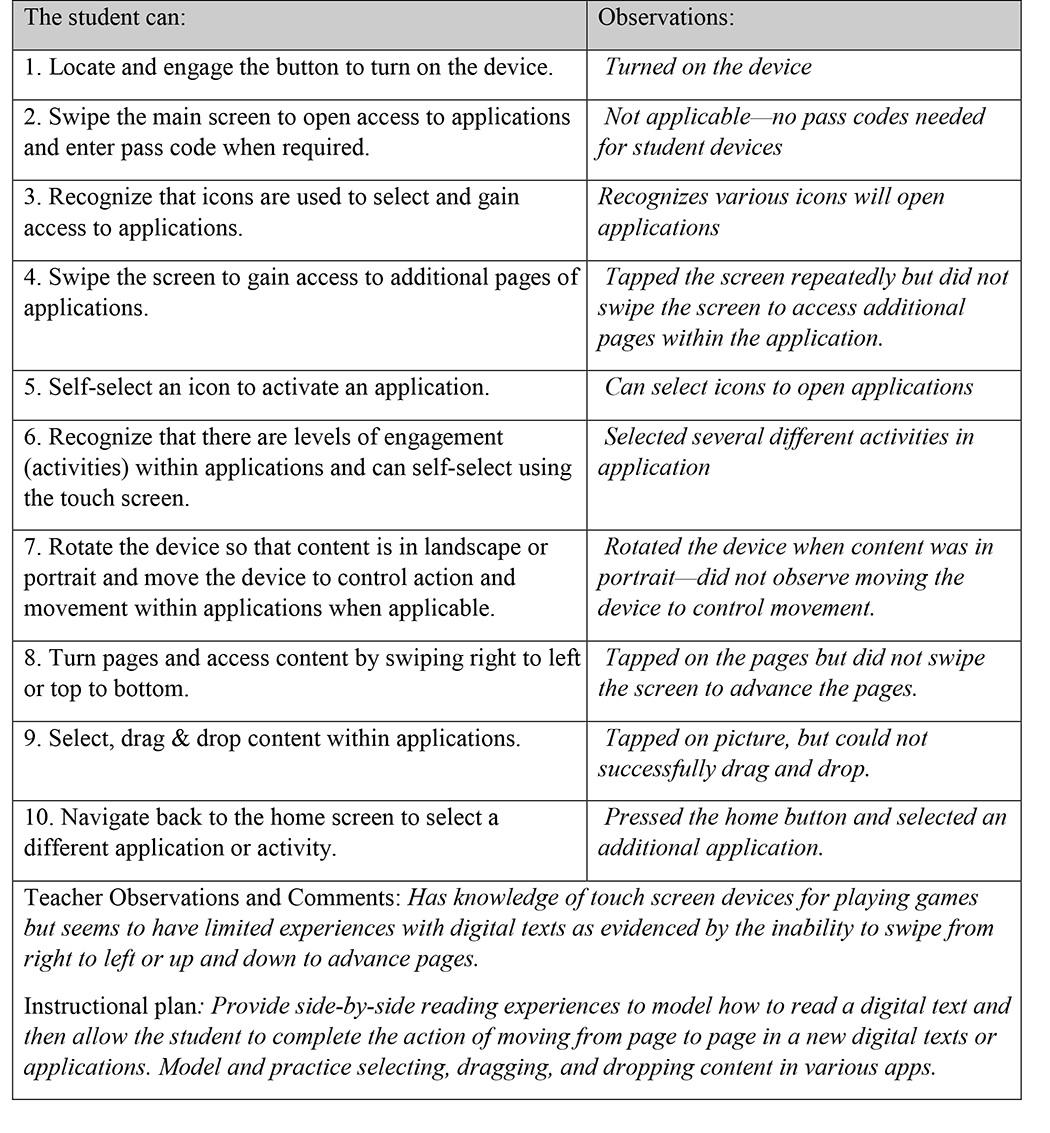
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Proficiency
This includes the ability to use various digital devices, software, and applications effectively to access, manage, and communicate information.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Digital literacy involves the ability to critically evaluate digital information, identify reliable sources, and apply problem-solving strategies to navigate and utilize digital environments.
Digital Content Creation
Digital literacy encompasses the skills to create and present digital content, such as online documents, presentations, multimedia, and even coding and programming.
Digital Collaboration and Communication
In the context of online learning, digital literacy involves the ability to engage in effective online communication, collaboration, and networking with peers, instructors, and the broader learning community.
Digital Citizenship and Ethics
Digital literacy also encompasses the understanding of digital rights, responsibilities, and ethical considerations, such as online privacy, security, and the appropriate use of digital resources.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
Given the rapidly evolving nature of digital technologies, digital literacy requires the ability to adapt to new tools and platforms, as well as a commitment to continuous learning and skill development.
Understanding these key components of digital literacy is essential for designing and implementing effective assessment strategies in online learning environments.
Challenges in Assessing Digital Literacy

Complexity and Multidimensional Nature of Digital Literacy
Digital literacy is a multifaceted concept that encompasses a wide range of skills and competencies. Assessing digital literacy can be challenging due to its complex and rapidly evolving nature, as well as the diverse contexts in which it is applied.
Lack of Standardized Assessment Frameworks
The absence of widely accepted and standardized assessment frameworks for digital literacy can make it difficult to measure and evaluate student proficiency consistently across different educational institutions and online learning programs.
Technological Barriers and Inequities
Access to digital technologies and the level of technological infrastructure can vary significantly among students, leading to disparities in their ability to demonstrate digital literacy skills. This can create challenges in designing and administering fair and inclusive assessments.
Contextual Factors and Transferability of Skills
The application of digital literacy skills is often context-dependent, and the transferability of these skills across different digital environments and tasks can be a complex challenge to address in assessment practices.
Adapting to Evolving Digital Landscape
The rapid pace of technological change and the continuous emergence of new digital tools and platforms require ongoing adaptation and refinement of assessment strategies to ensure their relevance and effectiveness.
Overcoming these challenges requires a comprehensive and thoughtful approach to digital literacy assessment, drawing on best practices and innovative assessment methods.
Effective Assessment Methods for Digital Literacy
Performance-Based Assessments
Performance-based assessments, such as hands-on tasks, simulations, and project-based evaluations, can effectively measure students’ ability to apply digital literacy skills in authentic, contextual scenarios.
Example: Students may be asked to create a digital presentation or a website that demonstrates their ability to research, organize, and present information using various digital tools and platforms.
Portfolio-Based Assessments
Digital portfolios, where students curate and showcase their digital work and reflections over time, can provide a comprehensive and longitudinal view of their digital literacy development.
Example: Students may be required to maintain a digital portfolio that includes a variety of digital artifacts, such as online documents, multimedia projects, and evidence of their participation in online discussions and collaborations.
Self-Assessments and Reflections
Incorporating self-assessment activities, where students reflect on their own digital literacy skills and identify areas for improvement, can foster metacognition and promote self-directed learning.
Example: Students may be asked to complete a digital literacy self-assessment survey or a reflective journal, where they evaluate their proficiency in various digital literacy components and set personal learning goals.
Rubric-Based Evaluations
Developing and utilizing comprehensive, rubric-based assessment tools can help evaluate students’ digital literacy skills in a structured and consistent manner.
Example: A rubric may include criteria such as information management, digital content creation, online communication, and digital citizenship, with clearly defined performance levels for each criterion.
Observation and Feedback
Direct observation of students’ digital literacy skills in action, combined with constructive feedback, can provide valuable insights into their strengths, challenges, and areas for growth.
Example: Instructors may observe students as they navigate online platforms, collaborate in virtual environments, or engage in digital content creation, and provide targeted feedback to support their development.
Peer-Assisted Assessments
Incorporating peer-assisted assessments, where students provide feedback and evaluate each other’s digital literacy skills, can foster collaboration, critical thinking, and a deeper understanding of the assessment criteria.
Example: Students may be asked to review and provide feedback on their peers’ digital presentations or collaborative projects, using a shared assessment rubric.
The effective integration of these assessment methods can provide a comprehensive and multi-dimensional evaluation of digital literacy, enabling educators to make data-driven decisions and support students’ ongoing development in the digital learning environment.
Role of Formative and Summative Assessments
Formative Assessments
Formative assessments are ongoing evaluations that provide feedback to both students and instructors, allowing for the identification of strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement throughout the learning process.
Examples of Formative Assessments:
- Online quizzes or self-checks to gauge understanding of digital literacy concepts
- Peer reviews of digital projects or presentations
- Instructor feedback on digital assignments or participation in online discussions
Formative assessments in digital literacy can help students adapt their learning strategies, while enabling instructors to adjust their teaching approaches and provide targeted support.
Summative Assessments
Summative assessments are typically conducted at the end of a learning unit or course, and they aim to evaluate the overall achievement and proficiency of students in digital literacy skills.
Examples of Summative Assessments:
- Capstone projects that demonstrate comprehensive digital literacy skills
- Standardized digital literacy exams or certifications
- Final digital portfolios showcasing students’ work and growth over time
Summative assessments can provide a holistic evaluation of students’ digital literacy competencies, informing instructional decisions, program-level improvements, and the certification or credentialing of digital literacy skills.
Integrating Formative and Summative Assessments
By combining formative and summative assessments, educators can create a comprehensive and balanced approach to digital literacy evaluation. Formative assessments can guide ongoing learning and instruction, while summative assessments can measure the overall attainment of digital literacy goals and standards.
Example: A digital literacy course may incorporate a series of formative assessments, such as periodic check-ins and peer reviews, to help students identify and address their learning needs. At the end of the course, a summative assessment, such as a capstone project or a final digital portfolio, can be used to evaluate the students’ overall digital literacy proficiency and readiness for future digital learning challenges.
The strategic integration of formative and summative assessments can provide a holistic understanding of students’ digital literacy development, informing instructional decisions and ensuring that learners are equipped with the necessary skills to succeed in the digital learning environment.
Technology Tools for Digital Literacy Assessments
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning management systems, such as Moodle, Canvas, or Blackboard, often include built-in assessment tools and features that can be leveraged to evaluate digital literacy skills. These platforms can facilitate the delivery of quizzes, surveys, and other interactive assessments, as well as the collection and management of digital portfolios and project-based work.
Digital Collaboration and Productivity Tools
Collaborative tools like Google Suite, Microsoft 365, or cloud-based document sharing platforms can be used to assess students’ abilities to work together, communicate effectively, and create digital content in a collaborative environment.
Multimedia and Presentation Tools
Tools for creating and presenting digital content, such as PowerPoint, Prezi, or Canva, can be used to evaluate students’ digital content creation skills, visual design abilities, and presentation skills.
Specialized Digital Literacy Assessment Platforms
There are also specialized digital literacy assessment platforms, such as DigitalLiteracy.gov or the ISTE Standards for Students, that provide comprehensive assessment frameworks, rubrics, and resources to evaluate digital literacy proficiency.
Learning Analytics and Data Visualization
Learning analytics tools and data visualization techniques can be employed to analyze and interpret the data collected from digital literacy assessments, providing valuable insights into students’ performance and areas for improvement.
Adaptive and Personalized Assessments
Emerging technologies, such as adaptive learning algorithms and personalized assessment platforms, can tailor digital literacy assessments to individual student needs, providing a more personalized and targeted evaluation experience.
The effective integration of these technology tools can streamline the assessment process, enhance the reliability and validity of the data collected, and support the continuous improvement of digital literacy education.
Incorporating Digital Literacy Assessments into the Curriculum
Aligning Assessments with Learning Objectives
Digital literacy assessments should be closely aligned with the learning objectives and competencies defined within the curriculum. This ensures that the assessments accurately measure the intended digital literacy skills and support the overall instructional goals.
Integrated and Ongoing Assessment
Digital literacy assessments should be seamlessly integrated throughout the curriculum, rather than being treated as isolated or standalone activities. This can involve incorporating digital literacy assessments into various course components, such as assignments, projects, and discussions.
Collaborative Assessment Design
Educators should collaborate with instructional designers, educational technologists, and subject matter experts to develop a comprehensive and well-rounded approach to digital literacy assessment. This collaborative effort can leverage diverse perspectives and expertise to create effective assessment strategies.
Scaffolded Assessments
Digital literacy assessments should be designed with a scaffolded approach, where the level of complexity and challenge gradually increases as students progress through the curriculum. This supports the development of digital literacy skills and ensures that assessments are appropriate for the learners’ abilities.
Providing Constructive Feedback
Incorporating detailed and constructive feedback into the digital literacy assessment process is crucial for supporting student learning and growth. Feedback should highlight students’ strengths, identify areas for improvement, and provide guidance on how to enhance their digital literacy skills.
Connecting Assessments to Real-World Applications
Aligning digital literacy assessments with real-world scenarios and applications can help students recognize the relevance and practical value of their digital literacy skills. This can include tasks that simulate workplace or everyday digital challenges.
Continuous Evaluation and Refinement
Regularly reviewing and refining the digital literacy assessment strategies is essential to ensure their continued effectiveness and relevance in the evolving digital landscape. Incorporating student feedback, monitoring assessment outcomes, and adapting assessment methods can help maintain the currency and relevance of the assessment practices.
By integrating digital literacy assessments thoughtfully and strategically into the curriculum, educators can foster the development of essential digital skills and support student success in the online learning environment.
Strategies for Improving Digital Literacy Among Students
Fostering a Digital Literacy-Focused Learning Environment
Creating a learning environment that actively promotes and supports the development of digital literacy skills is crucial. This can involve incorporating digital literacy-related activities, resources, and discussions throughout the curriculum, as well as encouraging a culture of digital exploration and collaboration among students.
Providing Targeted Skill-Building Opportunities
Offering targeted skill-building opportunities, such as workshops, tutorials, or micro-credentials, can help students enhance their digital literacy competencies in specific areas. These focused learning experiences can address gaps or areas of weakness identified through digital literacy assessments.
Promoting Digital Citizenship and Responsible Use of Technology
Integrating lessons on digital citizenship, online safety, and the ethical use of technology can empower students to become responsible and engaged digital citizens. This can involve discussions on privacy, cybersecurity, digital rights, and the social impact of technology.
Encouraging Peer-to-Peer Learning and Collaboration
Fostering opportunities for peer-to-peer learning and collaboration can create a supportive environment for students to share knowledge, provide feedback, and learn from one another’s digital literacy experiences.
Integrating Digital Literacy Across the Curriculum
Incorporating digital literacy-related content, activities, and assessments across various subject areas can help students recognize the relevance and applicability of their digital skills in diverse academic and professional contexts.
Providing Professional Development for Educators
Offering ongoing professional development opportunities for educators to enhance their own digital literacy skills and assessment strategies can ensure that they are equipped to effectively support and guide students in their digital learning journeys.
Leveraging Community and Industry Partnerships
Collaborating with community organizations, industry partners, and subject matter experts can provide valuable insights, resources, and mentorship opportunities to further strengthen students’ digital literacy competencies.
By implementing these strategies, educators can empower students to become confident, responsible, and proficient digital learners, well-prepared to navigate and succeed in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Analyzing Data from Digital Literacy Assessments
Data Collection and Management
Establishing effective data collection and management practices is crucial for deriving meaningful insights from digital literacy assessments. This may involve the use of learning management systems, data analytics platforms, or custom-built data management solutions to capture, organize, and store assessment data.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Analyzing the data collected from digital literacy assessments can reveal patterns and trends related to student performance, areas of strength and weakness, and the overall effectiveness of the assessment strategies. This can inform instructional decisions and guide the continuous improvement of digital literacy education.
Disaggregating Data
Disaggregating assessment data based on various demographic factors, such as age, gender, socioeconomic status, or prior digital experience, can provide valuable insights into potential equity gaps or disparities in digital literacy development. This information can inform targeted interventions and support strategies.
Correlating Digital Literacy with Academic Performance
Examining the relationship between digital literacy assessment results and overall academic performance can shed light on the impact of digital literacy skills on student success in the online learning environment. This can help educators prioritize digital literacy development as a key driver of academic achievement.
Benchmarking and Comparative Analysis
Comparing digital literacy assessment data with benchmarks, national or industry standards, or performance of peer institutions can provide valuable context and inform the continuous improvement of digital literacy assessment practices.
Communicating Findings and Insights
Effectively communicating the insights derived from digital literacy assessment data to key stakeholders, such as students, parents, administrators, and policymakers, can help build awareness, secure support, and drive meaningful change in digital literacy education.
By leveraging the data collected from digital literacy assessments, educators can make informed decisions, implement targeted interventions, and continuously enhance the quality and effectiveness of digital literacy education in the online learning environment.
Case Studies and Best Practices in Digital Literacy Assessment
Case Study: Implementing a Comprehensive Digital Literacy Program at a Virtual High School
A virtual high school, recognizing the critical importance of digital literacy, developed a comprehensive digital literacy program that spanned the entire curriculum. The program included:
- A digital literacy assessment framework aligned with national standards
- Formative assessments integrated into various course activities and assignments
- Summative assessments, such as a capstone digital portfolio, to evaluate overall digital literacy proficiency
- Ongoing professional development for teachers to enhance their digital literacy instruction and assessment skills
- Partnerships with local technology companies to provide mentorship and real-world learning experiences for students
The implementation of this comprehensive program resulted in significant improvements in students’ digital literacy skills, as well as increased engagement and academic success in the online learning environment.
Best Practices in Digital Literacy Assessment:
- Establish a Clear Assessment Framework: Develop a comprehensive digital literacy assessment framework that aligns with the specific learning objectives and competencies of the online learning program.
- Utilize Diverse Assessment Methods: Employ a combination of performance-based assessments, portfolio-based evaluations, and self-assessments to provide a well-rounded evaluation of digital literacy skills.
- Integrate Assessments Seamlessly: Incorporate digital literacy assessments throughout the curriculum, rather than treating them as standalone activities, to foster a culture of continuous digital learning and improvement.
- Provide Personalized Feedback: Ensure that students receive detailed and constructive feedback on their digital literacy assessments, empowering them to identify areas for growth and take an active role in their own skill development.
- Leverage Technology Tools: Utilize a range of technology tools and platforms to streamline the administration, data collection, and analysis of digital literacy assessments, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in the assessment process.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Engage students, educators, parents, and industry partners in the design and implementation of digital literacy assessments to foster a sense of ownership and accountability among all stakeholders.
- Offer Continuous Support and Resources: Provide ongoing support, resources, and targeted interventions for students who may require additional assistance in enhancing their digital literacy skills, promoting a growth mindset and a commitment to lifelong learning.
- Evaluate and Adapt Assessment Strategies: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of digital literacy assessment strategies, gather feedback from stakeholders, and make adjustments based on data-driven insights to continuously improve assessment practices.
By following these best practices and drawing inspiration from successful case studies, educators can design and deliver effective digital literacy assessments that empower students to thrive in a technology-driven world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital literacy is essential for success in online learning environments, as it equips students with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes needed to navigate and thrive in the digital world. Assessing digital literacy is a complex yet critical aspect of ensuring that students develop the necessary competencies to succeed academically and professionally.
Effective digital literacy assessments should encompass a variety of methods and tools, including formative and summative assessments, to provide a comprehensive evaluation of students’ skills and progress. By integrating digital literacy assessments into the curriculum, providing targeted skill-building opportunities, and analyzing assessment data, educators can tailor instruction to meet the diverse needs of learners and enhance overall digital literacy outcomes.
Promoting digital citizenship, encouraging collaboration, integrating digital literacy across the curriculum, and offering professional development for educators are key strategies for improving digital literacy among students. Leveraging community partnerships and implementing best practices in digital literacy assessment can further enhance students’ readiness for the digital age.
By investing in digital literacy assessments and prioritizing digital literacy education, institutions can empower students to become confident, responsible, and proficient digital learners. Through continuous evaluation, adaptation, and improvement of assessment strategies, educators can ensure that students are well-prepared to succeed in an increasingly digital world.
