Assessment is a crucial aspect of the learning process, as it helps educators gauge students’ progress, identify areas for improvement, and measure the overall effectiveness of their teaching strategies. In the realm of online learning, where traditional classroom dynamics are replaced by virtual interactions, the role of assessment becomes even more crucial. Two primary types of assessment are formative and summative assessment, each with its unique characteristics and benefits.
Definition of Formative Assessment
Formative assessment is an ongoing process that occurs throughout the learning journey, providing continuous feedback to both the student and the educator. It is designed to identify a student’s current level of understanding, pinpoint areas where they may be struggling, and guide the necessary adjustments to the teaching and learning process. Formative assessments are typically low-stakes, meaning they do not contribute significantly to a student’s final grade, but rather serve as a means to facilitate learning and growth.
Characteristics of Formative Assessment
- Ongoing and Iterative: Formative assessments are not limited to a single point in time but rather are conducted throughout the learning process, allowing for continuous feedback and improvement.
- Diagnostic: Formative assessments help identify specific areas where students are excelling or struggling, enabling educators to tailor their instructional strategies accordingly.
- Supportive: The primary goal of formative assessment is to support student learning by providing timely and actionable feedback, rather than solely evaluating performance.
- Flexible and Adaptable: Formative assessments can take various forms, from quizzes and discussions to self-reflections and peer evaluations, and can be adjusted based on the needs of the students and the learning objectives.
Examples of Formative Assessment Methods
- Quizzes and Polls: Short, low-stakes quizzes or polls can be used to gauge students’ understanding of key concepts throughout the learning process.
- Classroom Discussions: Engaging students in discussions, either synchronously or asynchronously, can provide valuable insights into their thought processes and level of comprehension.
- Exit Tickets: At the end of a lesson or module, students can be asked to respond to a brief set of questions or prompts, allowing educators to identify areas that may need further clarification.
- Peer and Self-Assessments: Encouraging students to evaluate their own work or provide feedback to their peers can foster critical thinking and self-reflection skills.
- Reflective Journaling: Asking students to regularly reflect on their learning experiences, challenges, and progress can help them identify personal areas for improvement.
Definition of Summative Assessment
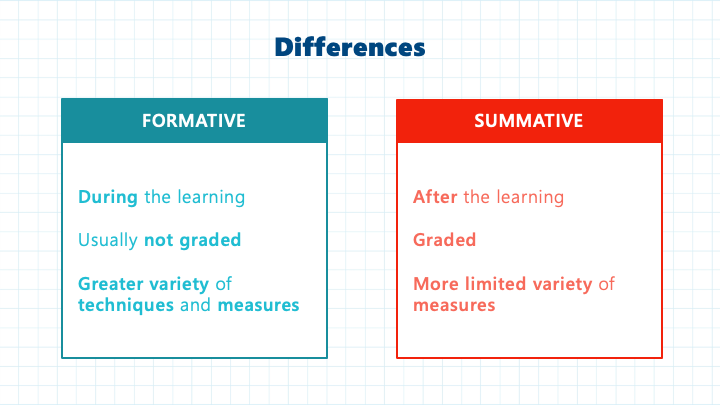
Summative assessment, on the other hand, is typically conducted at the end of a learning unit, course, or program, and is designed to measure the overall achievement of the student. These assessments are often high-stakes, contributing significantly to a student’s final grade or certification. Summative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of a student’s learning and are used to determine the effectiveness of the instructional strategies and the achievement of the intended learning outcomes.
Characteristics of Summative Assessment
- Evaluative: Summative assessments are primarily focused on evaluating and measuring student learning, rather than supporting the learning process.
- High-Stakes: The results of summative assessments often have significant consequences, such as determining a student’s final grade or eligibility for advancement.
- Comprehensive: Summative assessments are designed to provide a holistic evaluation of a student’s learning, covering a broader range of knowledge and skills.
- Standardized: Summative assessments may be standardized, allowing for comparison of student performance across different classes, schools, or educational systems.
Examples of Summative Assessment Methods
- Final Exams: Comprehensive exams administered at the end of a course or program to assess a student’s overall mastery of the subject matter.
- Research Papers or Projects: Lengthy assignments that require students to demonstrate their ability to apply the knowledge and skills they have acquired.
- Portfolios: Collections of student work that showcase their progress and achievements over a period of time.
- Capstone Experiences: Culminating projects or presentations that integrate and demonstrate a student’s learning across multiple courses or programs.
- Certification or Licensure Exams: High-stakes assessments that evaluate a student’s readiness for professional certification or licensure.
Key Differences between Formative and Summative Assessments
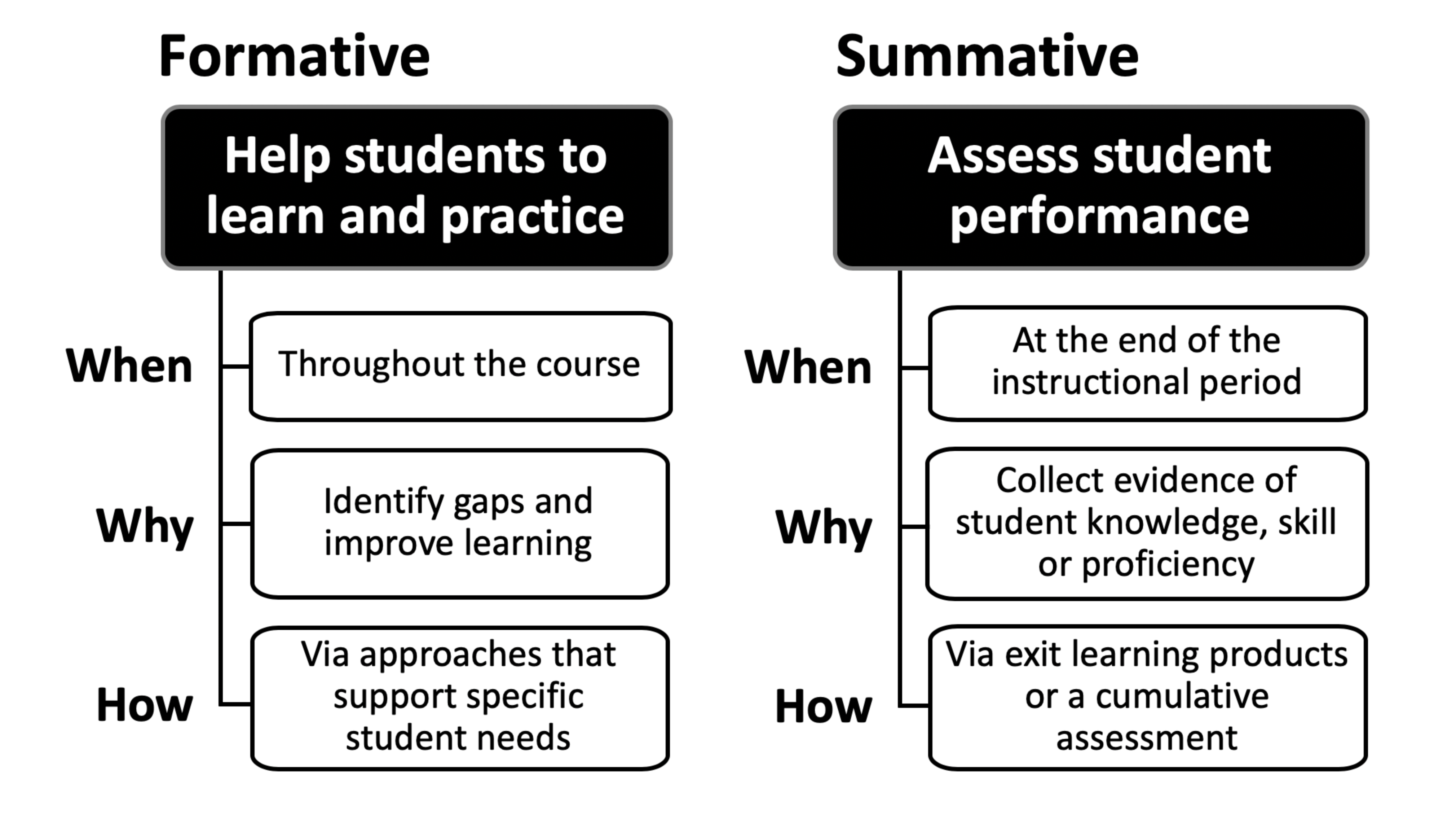
While both formative and summative assessments play important roles in the learning process, they differ in several key ways:
Purpose
- Formative Assessment: Designed to support and guide the learning process, identify areas for improvement, and inform instructional decisions.
- Summative Assessment: Focused on evaluating and measuring the final outcomes of learning, typically for the purpose of grading, certification, or accountability.
Timing
- Formative Assessment: Conducted throughout the learning process, providing ongoing feedback and opportunities for improvement.
- Summative Assessment: Administered at the end of a learning unit, course, or program, summarizing the overall level of student achievement.
Stakes
- Formative Assessment: Low-stakes, with limited or no impact on a student’s final grade or certification.
- Summative Assessment: High-stakes, with significant consequences, such as determining a student’s final grade or eligibility for advancement.
Feedback
- Formative Assessment: Provides specific, actionable feedback to guide and support student learning.
- Summative Assessment: Provides comprehensive feedback on a student’s overall performance, often with a focus on final outcomes.
Adaptation
- Formative Assessment: Allows for flexibility and adaptation of instructional strategies based on student needs and performance.
- Summative Assessment: Tends to be more standardized and less flexible, as the primary purpose is to measure and report on student achievement.
Benefits of Formative Assessment in Online Learning
In the context of online learning, formative assessment offers several key benefits:
1. Personalized Learning Experiences
- Diagnostic Insights: Formative assessments provide valuable insights into individual student strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences, enabling educators to tailor their instructional approaches accordingly.
- Adaptive Content Delivery: Based on the insights gained from formative assessments, online learning platforms can dynamically adjust the content, pace, and level of difficulty to better meet the needs of each student.
2. Timely Feedback and Intervention
- Immediate Feedback: Formative assessments can be designed to provide immediate feedback to students, allowing them to quickly identify areas for improvement and adjust their learning strategies.
- Early Intervention: By regularly monitoring student progress through formative assessments, educators can quickly identify struggling students and provide targeted support or interventions before significant learning gaps develop.
3. Fostering Self-Regulated Learning
- Metacognitive Awareness: Formative assessments encourage students to reflect on their own learning, develop a deeper understanding of their strengths and weaknesses, and take a more active role in the learning process.
- Intrinsic Motivation: The supportive and low-stakes nature of formative assessments can help foster a growth mindset, where students are motivated to learn and improve, rather than solely focused on grades or performance.
4. Continuous Improvement of Instructional Strategies
- Instructional Adaptations: Insights gained from formative assessments can help educators identify the effectiveness of their teaching methods and make timely adjustments to better support student learning.
- Curriculum Refinement: Aggregated data from formative assessments can inform curriculum development and revisions, ensuring that online learning materials and activities remain relevant and aligned with student needs.
Benefits of Summative Assessment in Online Learning
While formative assessment plays a crucial role in supporting student learning, summative assessment also offers valuable benefits in the context of online education:
1. Measuring Learning Outcomes
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Summative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of a student’s mastery of the course content, allowing educators to determine the overall effectiveness of their instructional strategies and the achievement of intended learning outcomes.
- Standardized Benchmarking: Summative assessments can be standardized, enabling the comparison of student performance across different online courses, programs, or educational institutions.
2. Accountability and Credentialing
- Grading and Certification: Summative assessments are often used to determine a student’s final grade or eligibility for certification, providing a clear and objective measure of their learning.
- Accreditation and Compliance: Summative assessment data can be used to demonstrate the quality and effectiveness of online learning programs to accrediting bodies and regulatory authorities.
3. Motivating Student Engagement
- Goal-Oriented Learning: The high-stakes nature of summative assessments can help motivate students to stay engaged and focused on achieving their learning objectives, particularly in self-paced or asynchronous online environments.
- Skill Development: Preparing for and performing well on summative assessments can encourage students to develop important skills, such as time management, critical thinking, and effective study habits.
4. Informing Continuous Improvement
- Program Evaluation: Summative assessment data can provide valuable insights into the overall effectiveness of online learning programs, informing future curriculum and instructional design decisions.
- Learner Analytics: Analyzing summative assessment results, in conjunction with other learner data, can help identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement in online learning environments.
Examples of Formative Assessment Methods in Online Learning
- Online Quizzes and Polls:
- Short, low-stakes quizzes that provide immediate feedback to students on their understanding of the course material.
- Polls that gauge students’ comprehension or opinions on specific topics, allowing educators to adjust their teaching accordingly.
- Discussion Forums:
- Asynchronous discussions that encourage students to actively engage with the course content, share their perspectives, and receive feedback from their peers and the instructor.
- Prompts or questions designed to elicit thoughtful responses and provide insights into students’ critical thinking skills.
- Self-Assessments and Reflections:
- Activities that prompt students to reflect on their own learning progress, identify areas for improvement, and set personal goals.
- Self-evaluation checklists or rubrics that allow students to assess their understanding of key concepts or the quality of their work.
- Peer Review:
- Opportunities for students to provide constructive feedback on their classmates’ assignments or projects, fostering collaboration and critical analysis skills.
- Peer-review activities can be facilitated through online platforms or discussion forums.
- Exit Tickets:
- Brief, end-of-lesson assessments that prompt students to summarize their key takeaways, identify areas of confusion, or pose questions for the instructor.
- Exit tickets can be delivered through online forms, surveys, or discussion boards.
- Multimedia Presentations:
- Assignments that require students to create and share multimedia presentations, such as video recordings or interactive slideshows, demonstrating their understanding of course concepts.
- Instructor feedback and peer comments can provide valuable formative assessment opportunities.
- Adaptive Learning Platforms:
- Online learning platforms that use data-driven algorithms to personalize the learning experience, adjusting the content and pace based on each student’s performance on formative assessments.
- Real-time feedback and adaptive learning paths help students identify and address their individual learning needs.
Examples of Summative Assessment Methods in Online Learning
- Final Exams:
- Comprehensive, high-stakes assessments administered at the end of a course or program to evaluate a student’s overall mastery of the subject matter.
- Online exams can be designed to include a variety of question formats, such as multiple-choice, short answer, or essay questions.
- Capstone Projects or Portfolios:
- Culminating assignments that require students to demonstrate their ability to apply the knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout the course or program.
- Portfolios can showcase a collection of student work, highlighting their progress and achievements over time.
- Research Papers or Dissertations:
- Lengthy, in-depth writing assignments that challenge students to engage in scholarly research, critical analysis, and effective communication.
- Online platforms can facilitate the submission, review, and feedback process for these types of summative assessments.
- Presentations or Demonstrations:
- Opportunities for students to showcase their learning through live or pre-recorded presentations, simulations, or demonstrations of their acquired skills.
- These assessments can be delivered synchronously or asynchronously, depending on the course format and learning objectives.
- Certification or Licensure Exams:
- High-stakes assessments that evaluate a student’s readiness for professional certification or licensure, often with significant implications for their future career prospects.
- Online proctoring and remote test-taking solutions can facilitate the administration of these types of summative assessments in online learning environments.
- Integrated Course Assignments:
- Larger, multifaceted projects or assignments that span multiple modules or units within a course, allowing students to demonstrate their ability to synthesize and apply the course content.
- These assessments can include a combination of written work, multimedia components, and collaborative elements.
- Adaptive Learning Assessments:
- Summative assessments that leverage adaptive learning technologies to tailor the assessment experience based on each student’s performance, ensuring a comprehensive and personalized evaluation of their learning.
- These assessments can provide detailed feedback and recommendations to both students and educators.
Implementing Formative Assessments in Online Courses
Effectively implementing formative assessments in online courses requires a thoughtful and strategic approach. Here are some key considerations:
1. Align with Learning Objectives
- Clearly Define Learning Objectives: Ensure that formative assessments are closely aligned with the specific learning objectives of the course or module, providing valuable feedback on students’ progress towards those goals.
- Integrate Assessments into Instructional Design: Incorporate formative assessments throughout the course, aligning them with the pacing and flow of the content delivery.
2. Leverage Technology
- Utilize Online Assessment Tools: Leverage a variety of online assessment tools, such as quizzes, polls, and discussion forums, to facilitate the delivery and management of formative assessments.
- Provide Immediate Feedback: Leverage the capabilities of online platforms to provide students with immediate, personalized feedback on their performance, enabling them to make timely adjustments to their learning strategies.
3. Foster Engagement and Collaboration
- Encourage Active Participation: Design formative assessments that actively engage students, such as peer-review activities or collaborative problem-solving tasks, to promote deeper learning and reflection.
- Facilitate Peer-to-Peer Feedback: Create opportunities for students to provide constructive feedback to their peers, fostering a sense of community and encouraging self-reflection.
4. Analyze and Respond to Data
- Monitor Student Progress: Regularly analyze the data collected from formative assessments to identify trends, patterns, and areas where students may be struggling.
- Adapt Instructional Strategies: Use the insights gained from formative assessments to make timely adjustments to the course content, teaching methods, and learning activities to better support student needs.
5. Communicate and Provide Actionable Feedback
- Offer Timely and Constructive Feedback: Provide students with clear, actionable feedback on their performance, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement.
- Encourage Self-Reflection: Prompt students to reflect on their own learning progress, identify personal areas for growth, and develop strategies for continuous improvement.
Implementing Summative Assessments in Online Courses
Effective implementation of summative assessments in online courses involves the following key considerations:
1. Align with Course Objectives and Outcomes
- Clearly Define Learning Outcomes: Ensure that summative assessments are designed to accurately measure the achievement of the course’s intended learning outcomes.
- Integrate Assessments into Course Structure: Incorporate summative assessments at strategic points throughout the course, such as the end of a module or the completion of the entire program.
2. Ensure Integrity and Validity
- Implement Secure Assessment Practices: Utilize online proctoring solutions, randomized question banks, and other security measures to maintain the integrity of summative assessments and prevent academic dishonesty.
- Develop Valid and Reliable Assessments: Design summative assessments that accurately and consistently evaluate the intended knowledge, skills, and competencies.
3. Leverage Technology for Efficiency
- Automate Grading and Feedback: Leverage online assessment platforms and scoring rubrics to streamline the grading process and provide timely feedback to students.
- Leverage Data Analytics: Analyze summative assessment data to identify areas for improvement, inform curriculum development, and enhance the overall quality of the online learning program.
4. Provide Meaningful Feedback and Support
- Offer Constructive Feedback: Provide students with detailed, meaningful feedback on their summative assessments, highlighting their strengths, areas for improvement, and actionable steps for future growth.
- Facilitate Remediation and Retake Opportunities: Consider offering students opportunities to retake or remediate summative assessments, ensuring they have the support needed to achieve the desired learning outcomes.
5. Ensure Alignment with Accreditation and RegulatoryBodies
- Adhere to Accreditation Standards: Ensure that summative assessments meet the requirements set forth by relevant accreditation bodies, ensuring the academic rigor and quality of the online learning program.
- Comply with Regulatory Guidelines: Align summative assessments with regulatory guidelines and standards governing online education, demonstrating compliance with industry regulations and best practices.
6. Promote Continuous Improvement:
- Gather Stakeholder Feedback: Collect input from students, instructors, and stakeholders on the effectiveness of summative assessments, using this feedback to drive continuous improvement efforts.
- Review and Revise Assessment Practices: Regularly review and revise summative assessment strategies based on feedback, data analysis, and evolving educational trends to enhance the overall assessment process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both formative and summative assessments play valuable roles in the online learning environment. Formative assessments offer ongoing feedback to guide student learning and inform instructional decisions, while summative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of student achievement and program outcomes. By effectively implementing a combination of formative and summative assessments in online courses, educators can create engaging, personalized, and impactful learning experiences for students.
Through a variety of assessment methods such as quizzes, discussions, projects, research papers, presentations, and exams, online learners have opportunities to demonstrate their understanding, apply their knowledge, and showcase their skills in diverse ways. Leveraging technology, fostering collaboration, providing actionable feedback, and ensuring alignment with learning objectives are essential principles for successful assessment implementation in online courses.
As online education continues to evolve and expand, incorporating innovative and effective assessment practices will be crucial in meeting the diverse needs and expectations of today’s learners. By embracing best practices in formative and summative assessment, educators can optimize the online learning experience, empower student success, and ultimately achieve the desired learning outcomes and program objectives.
